Our Science/ Seba Technology Disruption Framework/ In-Depth
Modelling Disruption

Technology is ‘practical knowledge’
The know-how with which to transform matter, energy, and information from less desirable configurations into more desirable ones.
Key Features
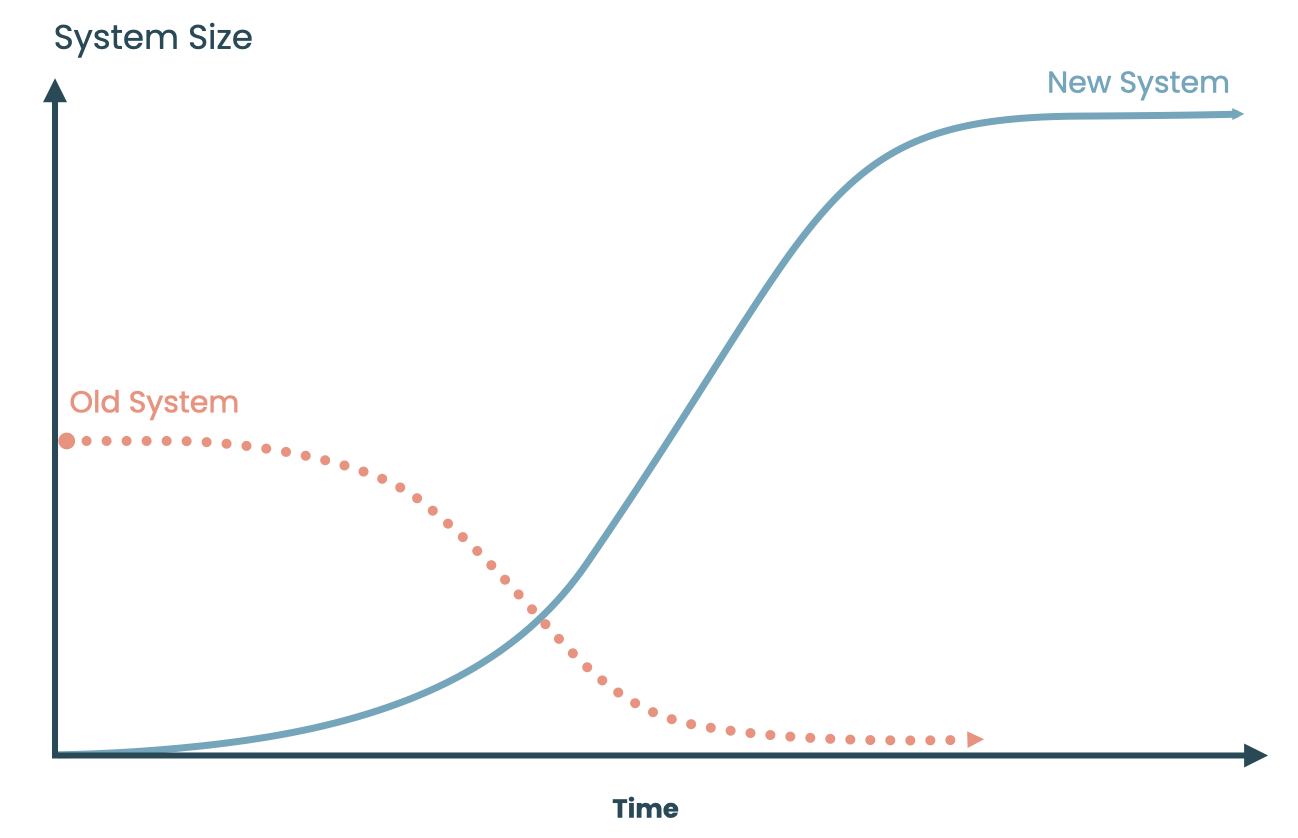
S-Curve
Adoption of a new technology (and the corresponding abandonment of an old technology) tends to trace a sigmoid trajectory over time.
This is because the underlying adoption rate tends to start slow before accelerating to a peak and then decelerating.
Asymmetry
The adoption S-curve of a new technology (and its underlying adoption rate bell curve), tends not to be symmetrical, but instead tends to be left skewed, such that more adoption occurs before the inflection from accelerating to decelerating growth than after the inflection.
Market Growth
New technology tends to grow the absolute size of the affected market, industry, or sector.
Duration
The bulk of the adoption growth (e.g. from 10% to 80%, as measured by market share) tends to occur within twenty years.
Key commonalities
New Products, Business Models, and Metrics
Disruptions of all kinds change the basis of competition and thus require:
1) New business models with which to create value with that product;
2) New metrics with which to measure and understand that product’s cost-capability; and
3) New institutions, policies, and rules to govern the utilization of that product.
Disruption Tends to Come from Outsiders
Incumbent incentives are aligned against investment in and adoption of new technology and new products.
Incumbent firms whose existing products dominate the market tend not to disrupt themselves.
New Possibilities
New technology creates new possibilities to explore with new products, new applications, new markets, new industries, and – though rarely – entirely new sectors of the global economy.
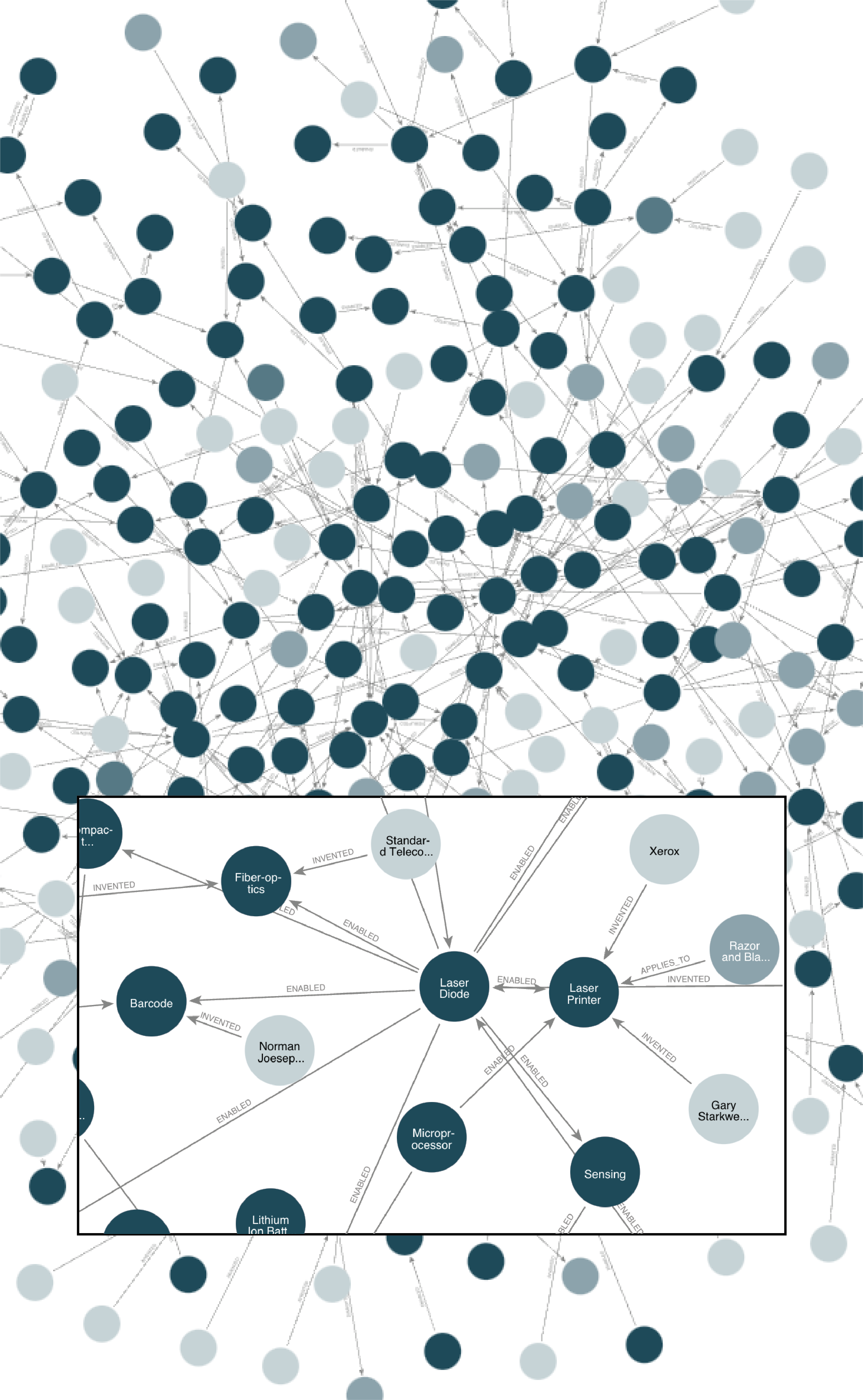
Cross-fertilization between technologies, both new and old alike, drives novel avenues of discovery and value creation.
Market Traumas
Market trauma is the sudden and extensive transformation of incumbent markets and their respective industries caused by new technologies early in the product adoption cycle.
The economics of incumbent industries can become abruptly unviable when disruptive products based on new technologies capture as little as a few percent of marketshare.
-min-2.png?%20Text%20570x770%20(1)-min-2.png&width=570&name=Website%20imagery%20-%20Large%20-%20Image%20%26%20Text%20570x770%20(1)-min-2.png?%20Text%20570x770%20(1)-min-2.png)
Dataset
At RethinkX, we have systematically gathered data around hundreds of examples of technology-driven disruptions.
Many of these fascinating disruption stories are recounted in The Pattern of Progress: How Radically Cheaper, Easier, Faster, Better Technologies and Ideas Rapidly Change the World
















%20(1).png?width=732&name=Copy%20of%20Website%20imagery%20-%20Featured%20Image%201200x628%20(15)%20(1).png)
.png?width=732&name=Untitled%20design%20(22).png)
.png?width=732&name=Untitled%20design%20(13).png)


